JavaScript - ArraysEg: const cars = ["Mahindra", "Tata", "BMW"];Why Use Arrays ? If you have a list of items (a list of car names, for example), storing the cars in single variables could look like this:
let car1 = "Mahindra";
let car2 = "Tata";
let car3 = "BMW";
However, what if you want to loop through the cars and find a specific one? And what if you had not 3 cars, but 300?
The solution is an array!
An array can hold many values under a single name, and you can access the values by referring to an index number.
Creating an Array :Using an array literal is the easiest way to create a JavaScript Array.
Syntax:
const array_name = [item1, item2, ...];
< !DOCTYPE html>
< html>
< body>
< h1>JavaScript Arrays< /h1>
< p id="demo">< /p>
< p id="demo1">< /p>
< p id="demo2">< /p>
< script>
//by creating array
const cars = [
"Mahindra",
"Tata",
"BMW"
];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = cars;
//by array index
const cars1 = [];
cars1[0]= "Jaguar";
cars1[1]= "Audi";
cars1[2]= "Suzuki";
document.getElementById("demo1").innerHTML = cars1;
//by new keyword
const cars2 = new Array("Volkwagon", "Rolls royce", "Lamborghini");
document.getElementById("demo2").innerHTML = cars2;
< /script>
< /body>
< /html>
Output :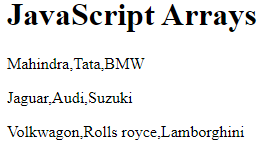 Accessing Array Elements : You access an array element by referring to the index number:
< !DOCTYPE html>
< html>
< body>
< h1>JavaScript Arrays< /h1>
< p id="demo">< /p>
< p id="demo1">< /p>
< p id="demo2">< /p>
< p id="demo3">< /p>
< p id="demo4">< /p>
< p id="demo5">< /p>
< p id="demo6">< /p>
< p id="demo7">< /p>
< script>
const cars = new Array("Volkwagon", "Rolls royce", "Lamborghini");
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = cars;
const cars1 = new Array("Lamborghini","Volkwagon", "Rolls royce");
document.getElementById("demo1").innerHTML = cars1[0]; //calling array by index
document.getElementById("demo2").innerHTML = cars1;
const cars3 = new Array("Lamborghini","Volkwagon", "Rolls royce");
cars3[1]="Jaguar"; //changing array by index
document.getElementById("demo3").innerHTML = cars3;
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
document.getElementById("demo4").innerHTML = fruits.toString();
const person = {firstName:"Banu prakash", lastName:"Elapan", age:25};
document.getElementById("demo5").innerHTML = person.firstName;
document.getElementById("demo6").innerHTML=cars3.length // Returns the number of elements
document.getElementById("demo7").innerHTML=cars3.sort()
< /script>
< /body>
< /html>
Output :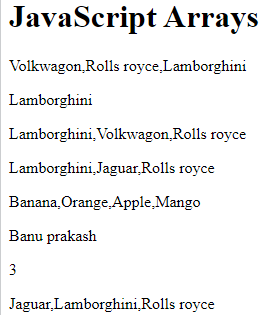 Loopig an array elements:
< !DOCTYPE html>
< html>
< body>
< h1>JavaScript Arrays< /h1>
< h2>Looping an Array< /h2>
< p id="demo">< /p>
< h2>For each loop< /h2>
< p id="demo1">< /p>
< script>
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
let objfruitLength = fruits.length;
let text = "< ul>";
for (let i = 0; i < objfruitLength; i++) {
text += "< li>" + fruits[i] + "< /li>";
}
text += "< /ul>";
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = text;
console.log("For each loop");
const animals = ["Lion", "Tiger", "Dog", "Cat"];
let text1 = "< ul>";
animals.forEach(myFunction);
text += "< /ul>";
document.getElementById("demo1").innerHTML = text1;
function myFunction(value) {
text1 += "< li>" + value + "< /li>";
}
< /script>
< /body>
< /html>
Output : Adding array elements : The easiest way to add a new element to an array is using the push() method:
< !DOCTYPE html>
< html>
< body>
< h1>JavaScript Arrays< /h1>
< h2>The push() Method< /h2>
< p>The push method appends a new element to an array.< /p>
< button onclick="myFunction()">Try it< /button>
< p id="demo">< /p>
< script>
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple"];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits;
function myFunction() {
fruits.push("Lemon");
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits;
}
< /script>
< /body>
< /html>
Output :JavaScript ArraysThe push() MethodThe push method appends a new element to an array. Methods for Array in JS:
Array length
Array toString()
Array at()
Array join()
Array pop()
Array push()
Array shift()
Array unshift()
Array delete()
Array concat()
Array copyWithin()
Array flat()
Array splice()
Array toSpliced()
Array slice()
Extra :
Search Methods
Sort Methods
Iteration Methods
Methods for searching array :
Array Find and Search Methods
Array indexOf()
Array lastIndexOf()
Array includes()
Array find()
Array findIndex()
Array findLast()
Array findLastIndex()
See Also:
Basic Methods
Sort Methods
Iteration Methods
Array Sort Methods :
Alphabetic Sort
Array sort()
Array reverse()
Array toSorted()
Array toReversed()
Sorting Objects
Numeric Sort
Numeric Sort
Random Sort
Math.min()
Math.max()
Home made Min()
Home made Max()
See Also:
Basic Methods
Search Methods
Iteration Methods
Array Iteration Methods :
Array iteration methods operate on every array item:
Array forEach
Array map()
Array flatMap()
Array filter()
Array reduce()
Array reduceRight()
Array every()
Array some()
Array from()
Array keys()
Array entries()
Array with()
Array Spread (...)
« Previous Next Topic » (JS - Arrow Functions) |
